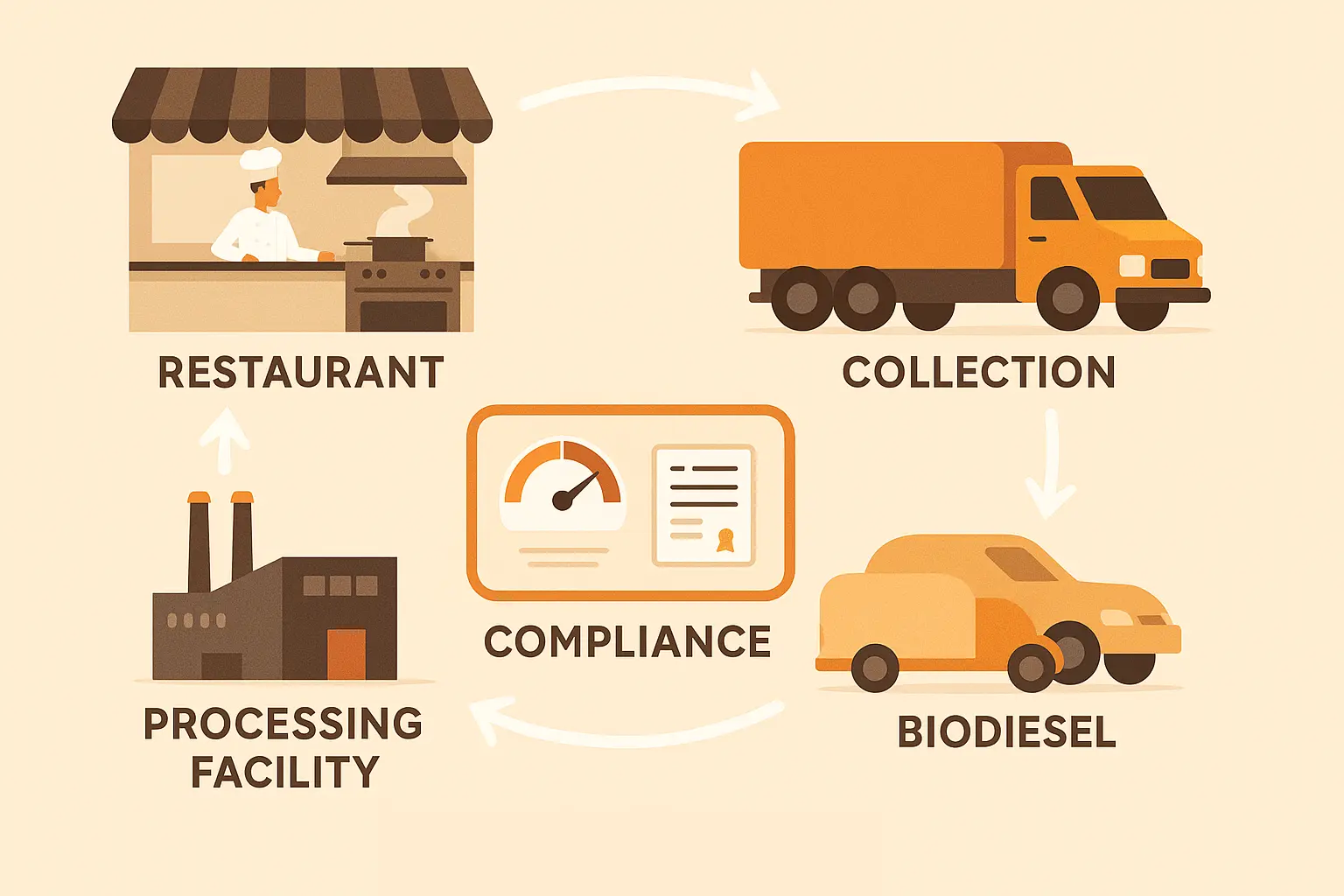
Regulatory compliance is important for commercial food service establishments—from small cafés to large industrial facilities that want to avoid fines and keep operations running smoothly. Many cities in the United States run mandatory FOG Control Programs that require record keeping, routine inspections, and proof of safe disposal for fats, oils, and grease.
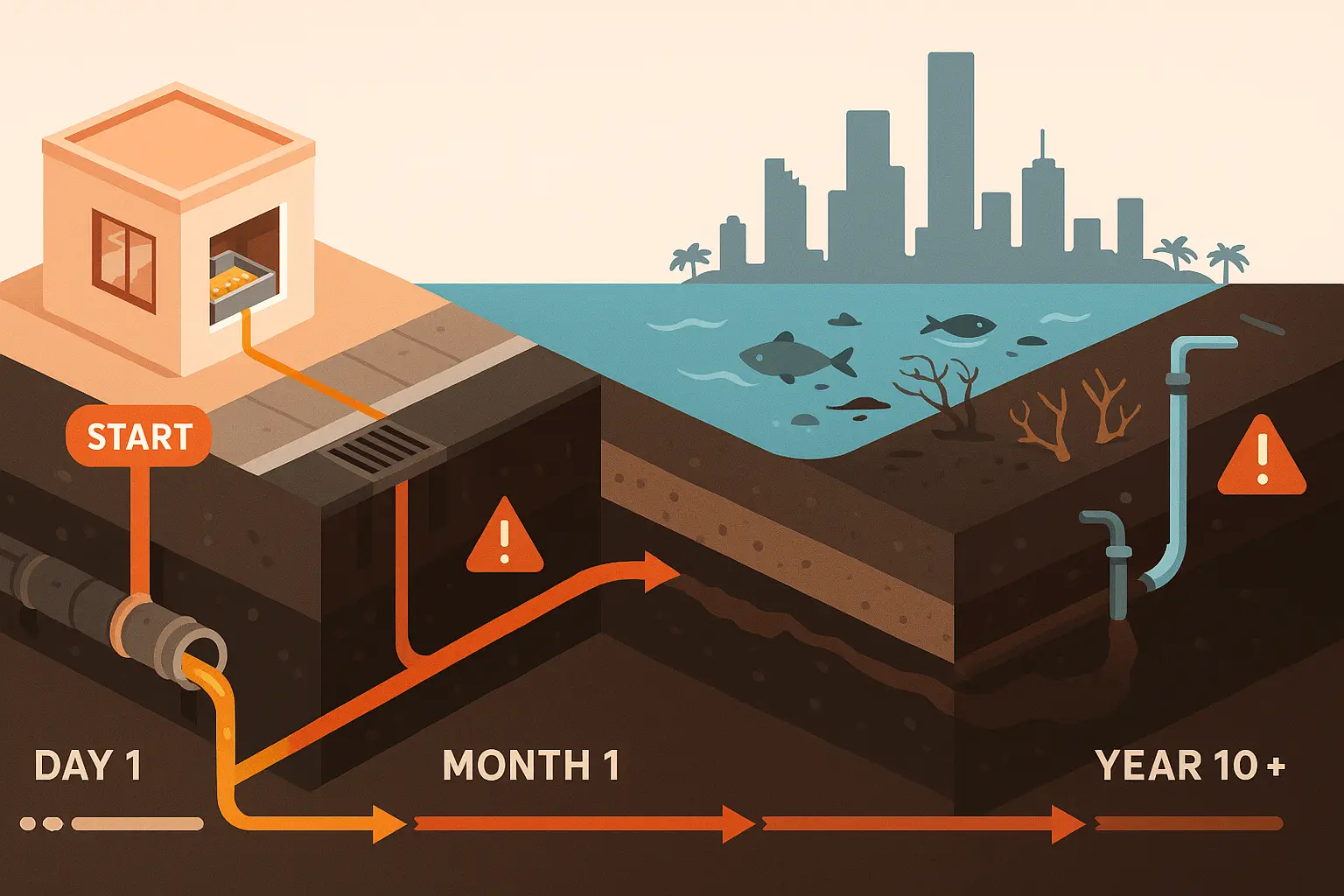
Key fact: Nearly half of sewage backups nationwide are caused by FOG clogs in the pipes, leading to costly sewer backups and cleanup efforts.
- The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) sets standards for kitchen exhaust systems, including thorough cleaning and routine maintenance to prevent grease buildup.
- Ignoring grease maintenance can lead to enforcement action, reputational damage, and potential closure by local authorities.
- The FOG Control Program usually includes educational components for businesses and offers guidance on safe FOG discharge.
Grease Traps — The 1/4 Rule
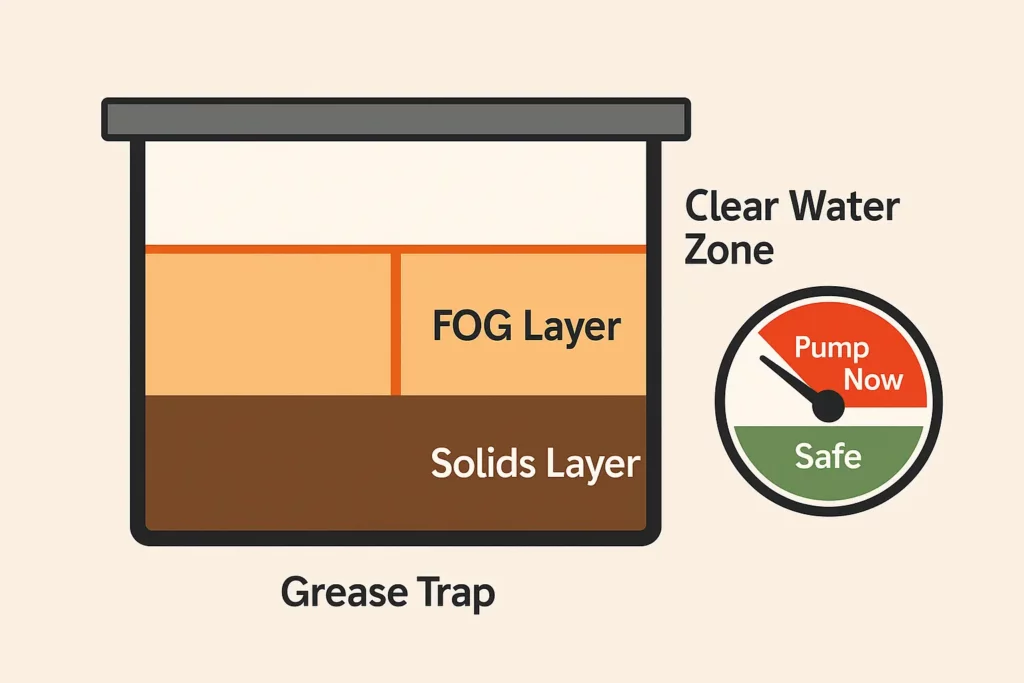
Grease traps stop FOG from reaching the sanitary sewer system, preventing blockages and maintaining compliance. To stay compliant:
- Follow the 1/4 Rule — pump the trap when it is one‑quarter full. Regular maintenance helps prevent clogs in grease traps and keeps the system flowing.
- Regular maintenance prevents odors, slow drainage, and costly repairs.
- Schedule extra cleanings during high‑volume months and keep every pump‑out ticket on file to satisfy inspectors.
- Scrape food scraps and excess grease from pans before washing to reduce trap load.
Investing in professional grease trap cleaning services ensures full compliance with maintenance regulations and avoids surprises during an inspection.
Kitchen Exhaust Cleaning & Fire Safety
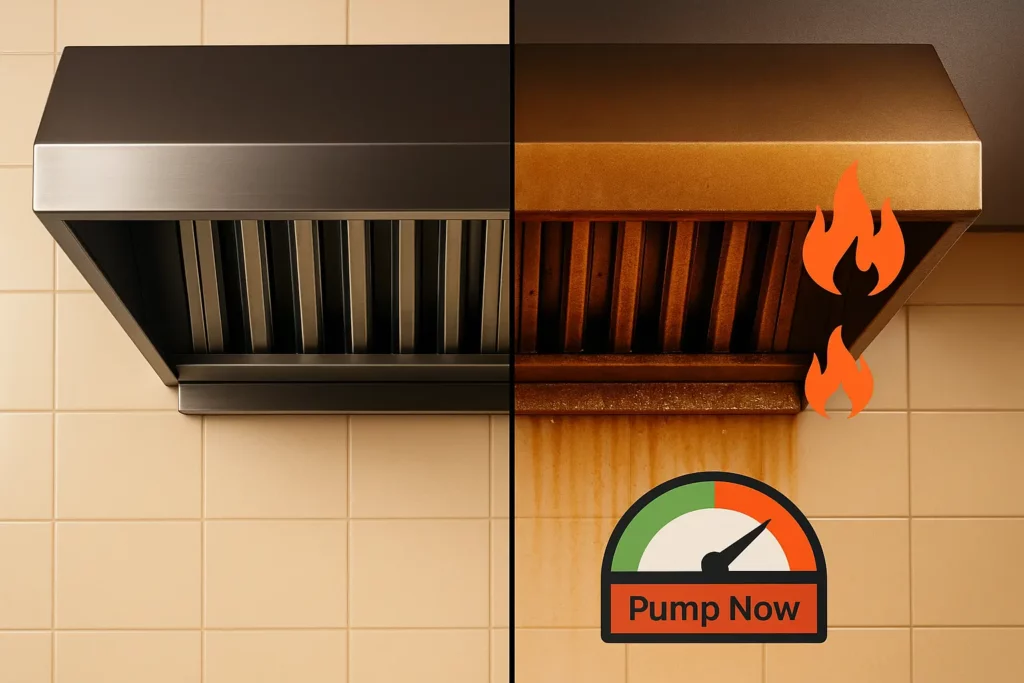
Compliance hinges on thorough cleaning and routine cleaning schedules that also apply to other high volume commercial cooking operations. A compliance‑ready plan includes:
- Routine cleaning of hoods, ducts, and fans using advanced tools and proper access panels, ensuring technicians can reach hard to reach areas and remove hidden grease.
- Document every visit; local health and fire departments check for filter‑maintenance logs during safety audits.
- Professional filter exchange services capture grease particles, prevent them from entering exhaust ducts, and provide written proof of service.
- Neglected filters reduce airflow, create uncomfortable work zones, and increase fire hazards.
Tip: Restaurants that do not maintain their fire‑prevention systems risk heavy fines or closures after a failed inspection.
Exhaust System Design & Efficiency
A well‑designed duct system and fan layout reduces grease laden vapors, boosts system efficiency, and lowers ongoing maintenance costs.
- Ensure the design meets NFPA fire‑safety standards.
- Plan for regular inspections to confirm components stay in optimal performance.
- Address overlooked aspects (elbows, long horizontal runs) where grease may accumulate.
Food Scraps Management
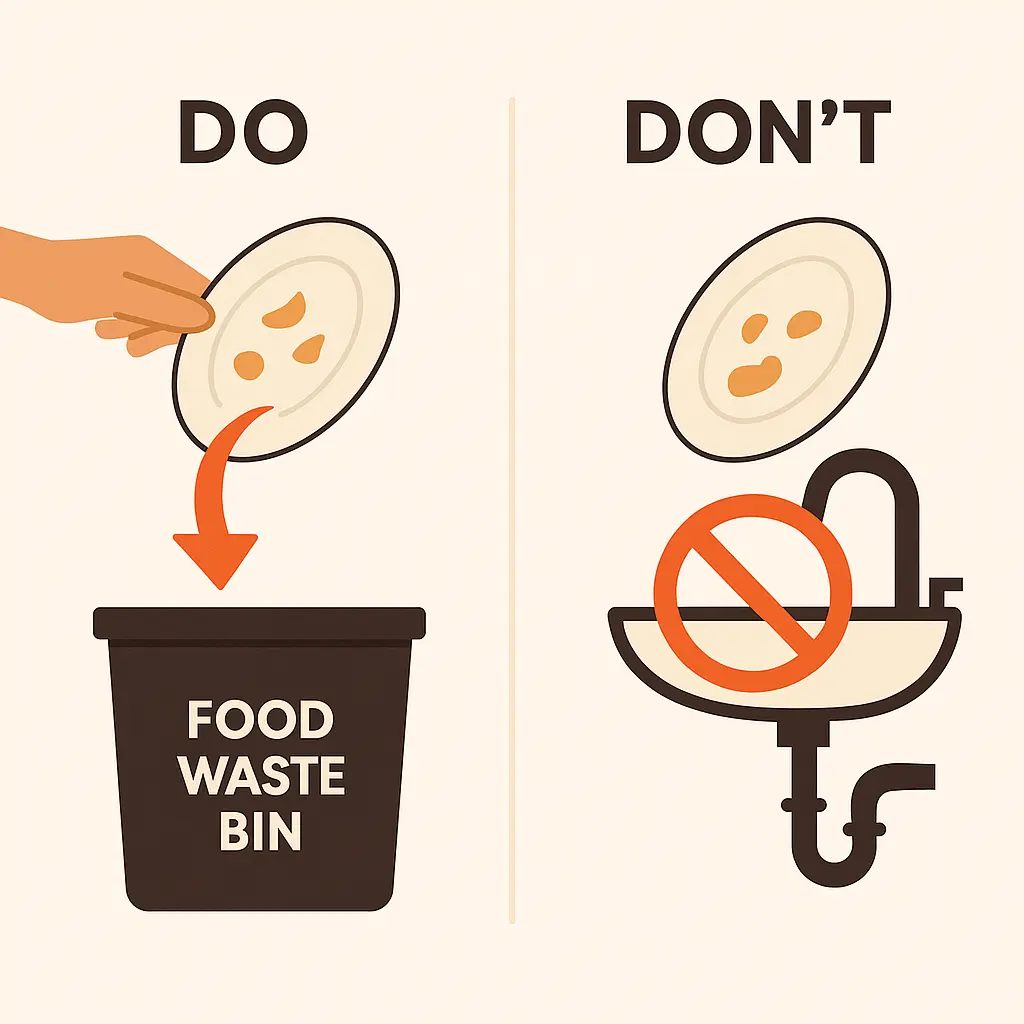
Improper disposal of food scraps and other debris is a significant problem that can introduce more grease into traps and sewers. Blockages in waste pipes caused by grease can lead to sewer back-ups that flood residences, businesses, city streets, and sidewalks with untreated raw sewage.
- Train staff to scrape plates and cookware before washing. Scraping FOGS from plates and cookware before washing can reduce grease accumulation in traps.
- Provide dedicated bins for solid waste and schedule timely pickups.
- Keep wash‑water runoff out of storm drains; wash mats and pans in designated wash areas connected to the sanitary sewer line, never outside.
Record Keeping & Documentation
Ensuring compliance through accurate record keeping proves regulatory compliance and reduces liability.
- Log every trap pump‑out, exhaust cleaning, and filter change.
- Keep manifests on site for at least three years (many programs require longer).
- Review logs monthly to track trends and schedule preventive service before issues arise.
Management Practices & Staff Training
Effective management practices for maintaining a clean and safe facility tie the checklist together.
- Assign a compliance champion to oversee FOG, fire‑safety, and cleaning schedules.
- Provide quarterly refreshers on spill response, waste cooking oil storage, and emergency procedures.
- Use visual reminders (checklists, QR codes) near traps, hoods, and recycling bins.
Importance of Regular Maintenance
Regular maintenance is essential for commercial food service establishments to ensure the longevity and efficiency of their equipment, including kitchen exhaust systems. The National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) emphasizes the importance of routine cleaning and maintenance to prevent grease buildup and reduce fire risks. By scheduling regular cleanings and inspections, food service establishments can identify potential issues before they become major problems, reducing the risk of fire hazards and ensuring operations run smoothly. Additionally, regular maintenance can help prevent increased maintenance costs and environmental damage caused by neglected exhaust systems.
Ensuring a Safe Working Environment
Ensuring a safe working environment is critical for commercial kitchens and industrial facilities. This can be achieved by implementing enhanced safety measures, such as regular cleaning and maintenance of exhaust systems, ducts, and other equipment. By reducing grease buildup and other contaminants, food service establishments can minimize the risk of fire hazards and create a safer environment for employees and customers. Furthermore, regular cleaning and maintenance can help prevent the accumulation of grease-laden vapors, which can pose significant health risks. Care must be taken when washing exhaust systems, as the combination of chemicals and grease can cause serious environmental problems. By prioritizing safety and maintenance, food service establishments can maintain a clean and sanitary environment, reduce fire risks, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards.
Environmental Impact & Community Stewardship
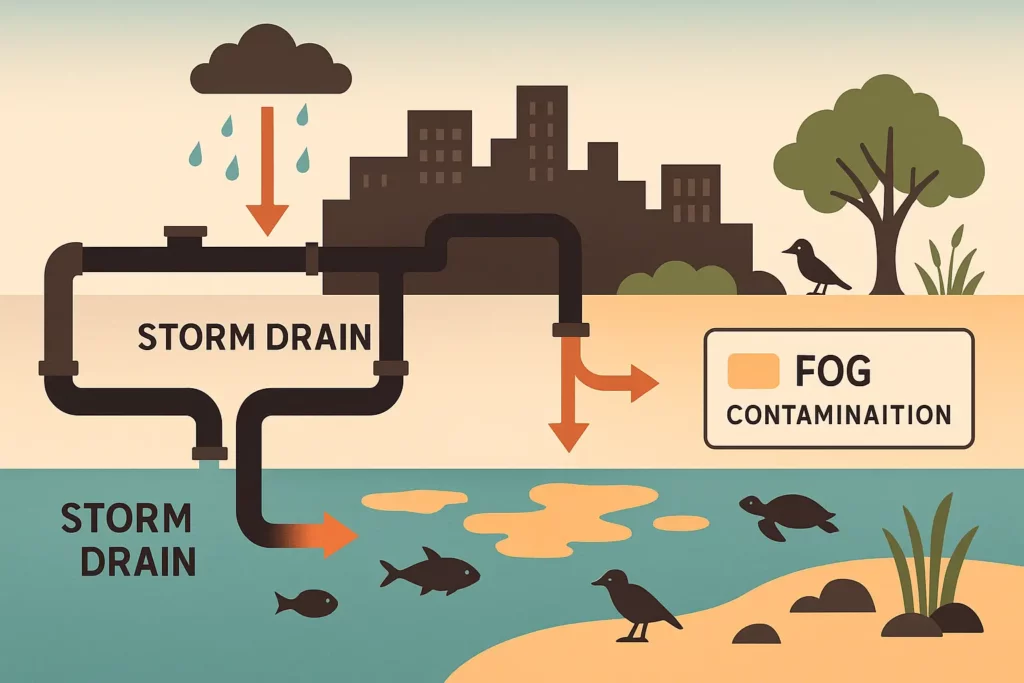
Grease that reaches storm sewers can discolor water, kill fish, and cause odors. Blocked pipes can flood homes and streets with raw sewage. Grease that enters storm sewers can travel to nearby streams, discolor the water, kill fish and plants, and create foul odors.
- Proper FOG disposal protects the environment, prevents costly sewer backups, and demonstrates community responsibility.
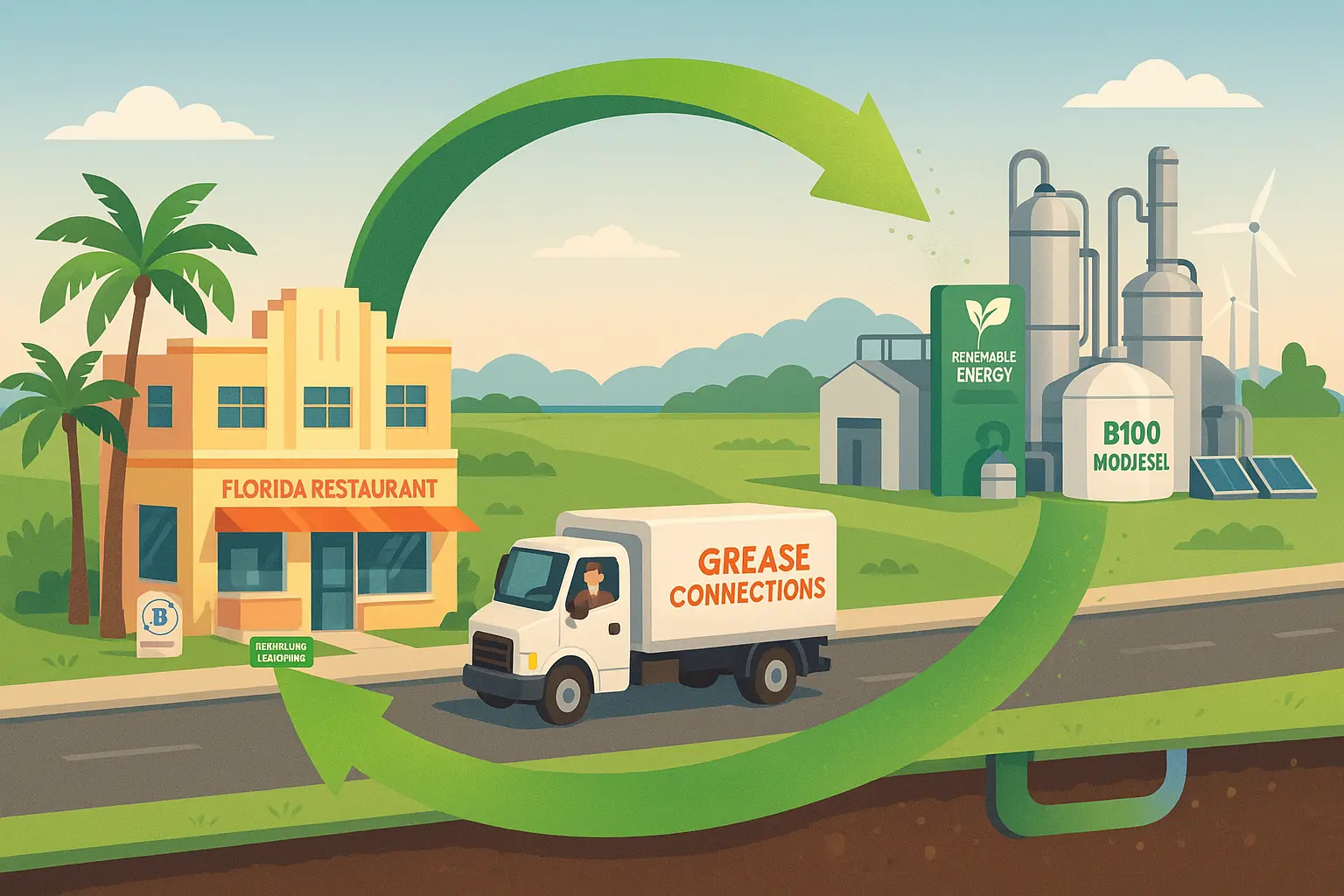
- Participating in local recycling programs turns waste cooking oil into biofuel, aligning the restaurant with broader environmental protection goals.
Waste Cooking Oil Disposal & Recycling
Properly managing waste cooking oil and chemicals keeps FOG out of sanitary sewers and storm drains, reducing fire risks and avoiding expensive pipe repairs.
- Store waste oil in leak‑proof drums away from other equipment.
- Use a trusted used cooking oil collection company for scheduled pickups; these services provide manifests for inspectors.
- Never pour oil into sinks—FOG cools, hardens, and causes sewer pipes to clog, leading to costly repairs.
Ultimate FOG Compliance Action List
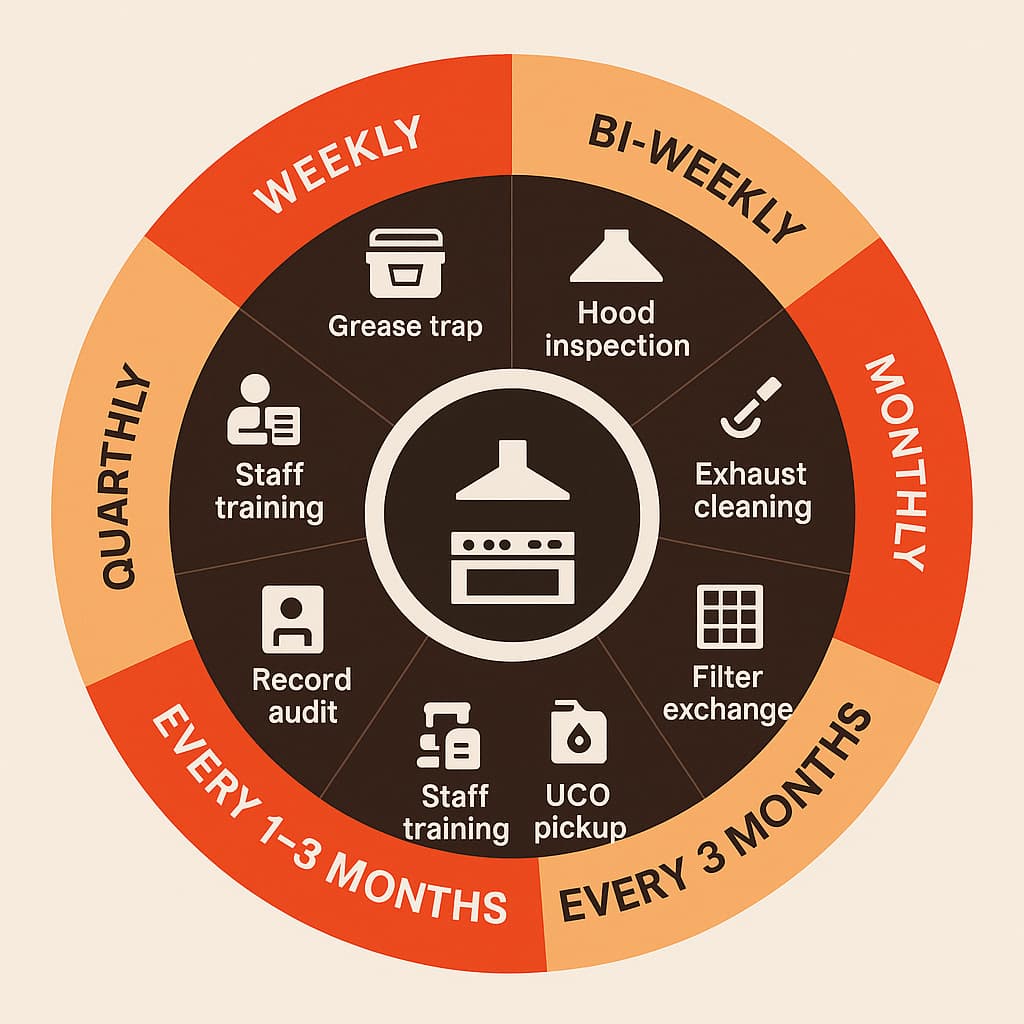
| Task | Frequency | Proof Required |
|---|---|---|
| Pump grease trap (1/4 Rule) | Every 1–3 months | Pump‑out ticket |
| Inspect hoods & ducts | Monthly | In‑house log |
| Professional exhaust cleaning | 3–6 months | Certified report |
| Filter exchange | Weekly | Service invoice |
| Waste UCO pickup | Bi‑weekly | Recycling manifest |
| Staff FOG training | Quarterly | Attendance sheet |
| Record audit & file backup | Monthly | Updated binder/cloud folder |
Proper disposal and recycling of waste cooking oil are crucial to maintaining a safe and efficient kitchen. Using hot water can help prevent grease from hardening and causing blockages in your plumbing system. Regular maintenance and adherence to cleaning regulations can save you from potential legal hot water, such as fines or business closure.
Best Practices for Food Service Establishments
To maintain a clean, safe, and efficient environment, food service establishments should adopt best practices for grease management and maintenance. This includes regular cleaning and inspection of grease traps, kitchen exhaust systems, and other equipment. Food service establishments should also prioritize the proper disposal of food scraps, waste cooking oil, and other contaminants to prevent grease buildup and minimize the risk of fire hazards.
By implementing these practices, food service establishments can ensure compliance with regulatory standards, reduce the risk of enforcement action, and maintain a trusted partner reputation. Additionally, regular record keeping and management practices can help food service establishments track their maintenance and cleaning schedules, ensuring long-lasting performance and superior results. By prioritizing these best practices, food service establishments can create a safer environment, reduce costs, and maintain a high level of efficiency and effectiveness.
Conclusion
Avoiding FOG fines starts with planning. Follow the 1/4 Rule, schedule thorough cleaning for traps and hoods to ensure they are properly cleaned and compliant, maintain detailed records, and train staff. With this checklist, commercial kitchens operate safely, protect the environment, and pass every inspection.
Disclaimer
This checklist covers health‑ and safety related topics for food service establishments and commercial buildings, emphasizing the importance of maintaining cleanliness and safety. It is for informational purposes only and is not legal or engineering advice. Always consult certified professionals and local regulators.